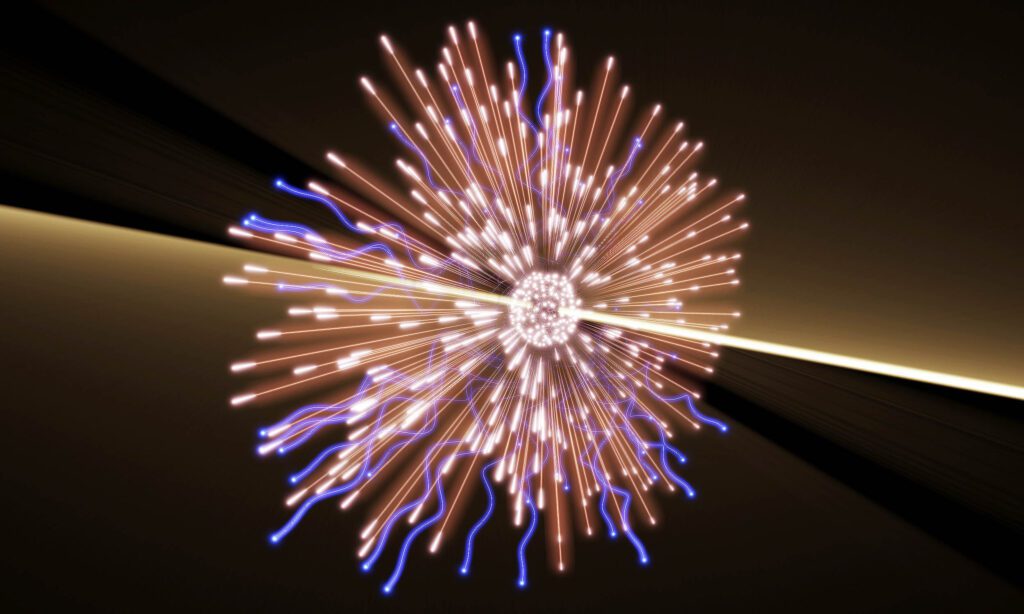
Scientists have announced a groundbreaking discovery in neutrino physics: the detection of an exceptionally energetic neutrino named KM3-230213A, which was observed by the ARCA detector of the KM3NET project in the Mediterranean. This neutrino, with an estimated energy equivalent to that of about 220 million people, marks a significant milestone in neutrino astronomy, allowing researchers to explore new astrophysical phenomena.
The KM3NET collaboration consists of over 360 experts from 68 institutions across 21 countries, working to study ultra-high energy neutrinos that may originate from extreme cosmic events such as supernova remnants or interactions of cosmic rays. The ARCA and ORCA detectors use advanced technology to capture the faint light generated when neutrinos collide with water molecules, enabling scientists to map their trajectories.
Despite being incomplete, the ARCA site successfully detected this rare event, indicating the potential for future discoveries as the network expands. Researchers continue to investigate whether this particular neutrino was generated by a cosmic phenomenon or from an active celestial body. The ongoing work is expected to enhance understanding of the universe’s forces and improve the identification of the origins of these cosmic particles. The findings have been published in the journal Nature.
Source link