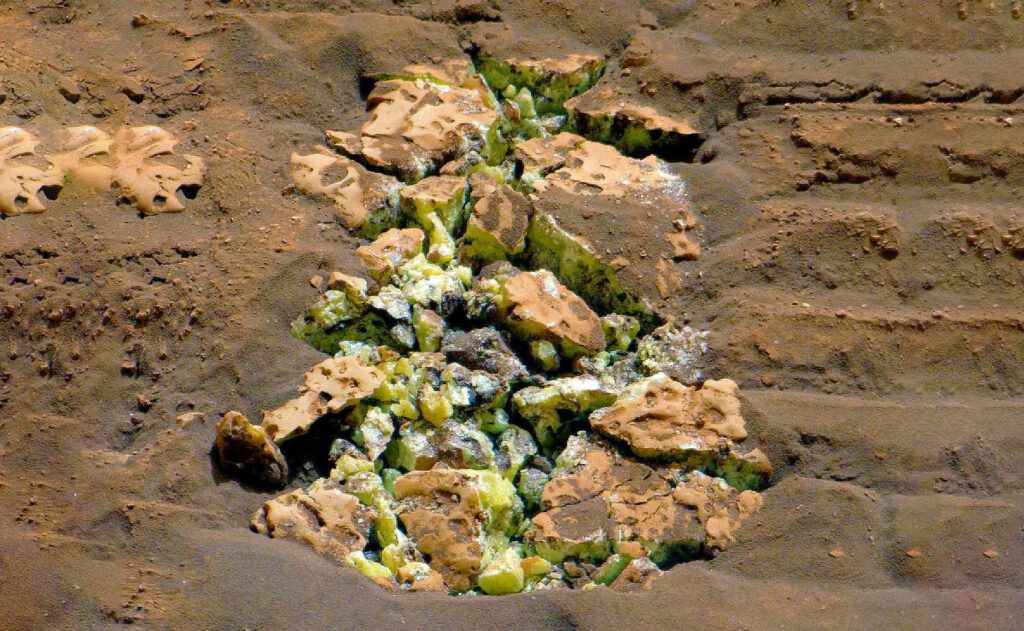
On May 30, 2024, NASA’s Curiosity Mars Rover made an unexpected discovery when it encountered a field of pure sulfur crystals on the Martian surface—an unprecedented finding. Project scientist Ashwin Vasavada described this as an “oasis in the desert,” emphasizing the excitement of discovering something so unusual. Sulfur, while not new to Mars (previously found as components in minerals), has now been identified in its elemental form, which suggests particular conditions for its formation that were not previously associated with this area.
The presence of sulfur is significant for understanding potential life on Mars, as certain Earth microorganisms utilize sulfur compounds as energy sources. While sulfur alone does not confirm the existence of life, its association with other elements crucial for life enhances possibilities. The discovery also sheds light on Mars’ geological history, including the potential for ancient lakes or hydrothermal systems.
Curiosity has been investigating the layered terrains of Mount Sharp for over seven years, examining minerals, including sulfates, that indicate past climatic changes. The Gediz Vallis channel, in particular, has provided insights into dynamic geological processes and interactions between water and rock.
As Curiosity continues to drill and analyze samples, scientists hope to uncover more about Mars’ chemical environment and its capacity to support life, thus deepening our understanding of the planet’s history and its potential for past life. Each new finding encourages a reevaluation of previous assumptions about Mars, as the rover continues its exploration of this intriguing landscape.
Source link