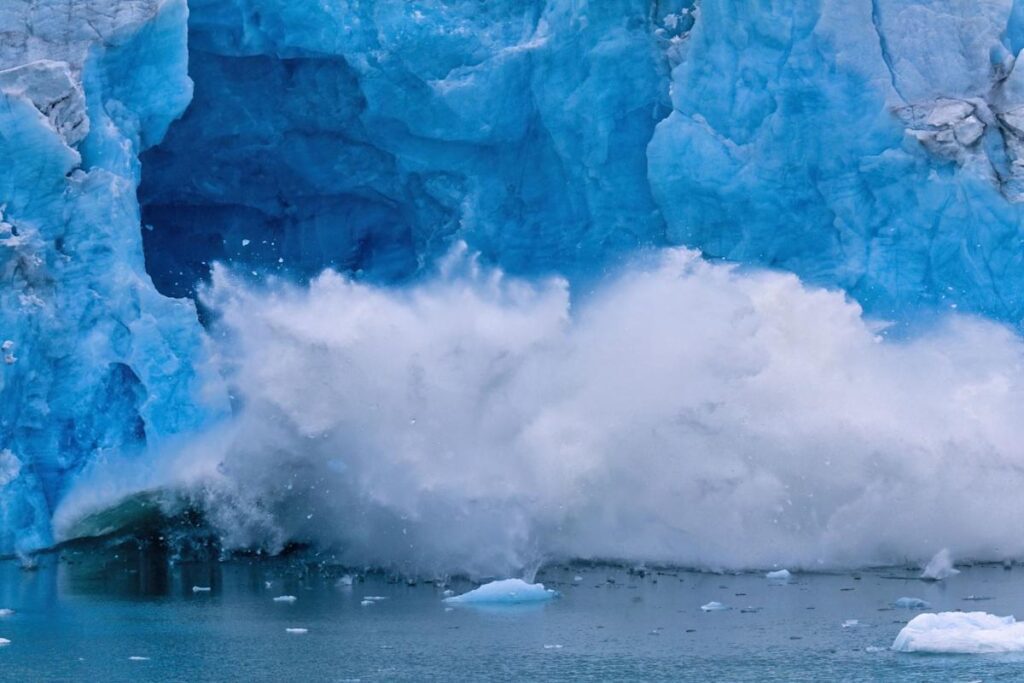
An international team of scientists has discovered a link between melting Arctic Ocean ice and global weather patterns, impacting regions as distant as California and Europe. This connection, known as teleconnections, refers to atmospheric phenomena that affect widely separated locations. The study, involving researchers from several countries, highlights how Arctic sea ice loss contributes to significant changes in weather, such as causing dry winters in the southwestern United States and wetter conditions in the western Mediterranean. The researchers developed a method to assess these impacts over decades without artificially manipulating sea ice conditions.
Lead author Ivana Cvijanovic emphasizes the need for understanding these remote effects, as previous studies often focused on long-term or combined impacts. The findings demonstrate similarities with recent severe weather events, such as the California drought from 2012-2016. The loss of Arctic sea ice not only accelerates global warming but also disrupts weather patterns and threatens marine ecosystems, like microscopic organisms crucial to food networks.
Efforts to mitigate this issue include innovative projects by Dutch startups aiming to restore polar ice caps by creating a reflective surface layer. Addressing climate change requires a transition to renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions through technology like solar panels and induction stoves. Rising sea levels, projected to impact the U.S. significantly by 2100, further underscore the importance of addressing Arctic ice loss proactively.
Source link